
Hi {{ first name | friend}},
What if your mitochondria cared less about how long you train and more about what signal you send?
At the cellular level, your body doesn’t see "cardio" or "strength training" the way we do. It sees mechanical stress (tension on muscle fibers, shear forces) and chemical stress (AMPK activation, changes in ATP/ADP ratios, reactive oxygen species, etc.). Both ultimately converge on the same control knobs – like PGC-1α, mTOR, and mitochondrial biogenesis – but they get there in very different ways.
In this edition of HEALTH HACK, we look at how to “talk” to your mitochondria using two main languages:
The mechanical route – load, intensity, and movement
The chemical route – molecules and pathways that can mimic or amplify training signals
The goal: help you understand which levers you’re already pulling, which ones you’re neglecting, and how to design a smarter, evidence-aligned mitochondrial strategy.
QUICK POLL
Which "Mitochondrial Lever" Are You Pulling Most Right Now?
- Mechanical load – resistance training, HIIT, sprints, zone 2, etc.
- Chemical signaling – supplements or drugs (e.g., NAD⁺ boosters, GLP-1s, metformin, “exercise mimetics”)
- Environmental hormesis – cold exposure, sauna, fasting, heat, hypoxia, etc.
- Stacking signals – a deliberate mix of 1, 2, and 3
- None (yet) – I’m still in the “observing and learning” phase
In a future issue, we’ll break down what the research says about the most effective combinations based on what most readers are actually doing.
-LONGEVITY PLAYBOOK-
If this helps, consider forwarding it to one person who is too busy to exercise.
Subscribe here: https://newsletter.health-hack.com
1 Minute of This = 9 Minutes of That?
If You're Busy, You’re Going to Love This New Science
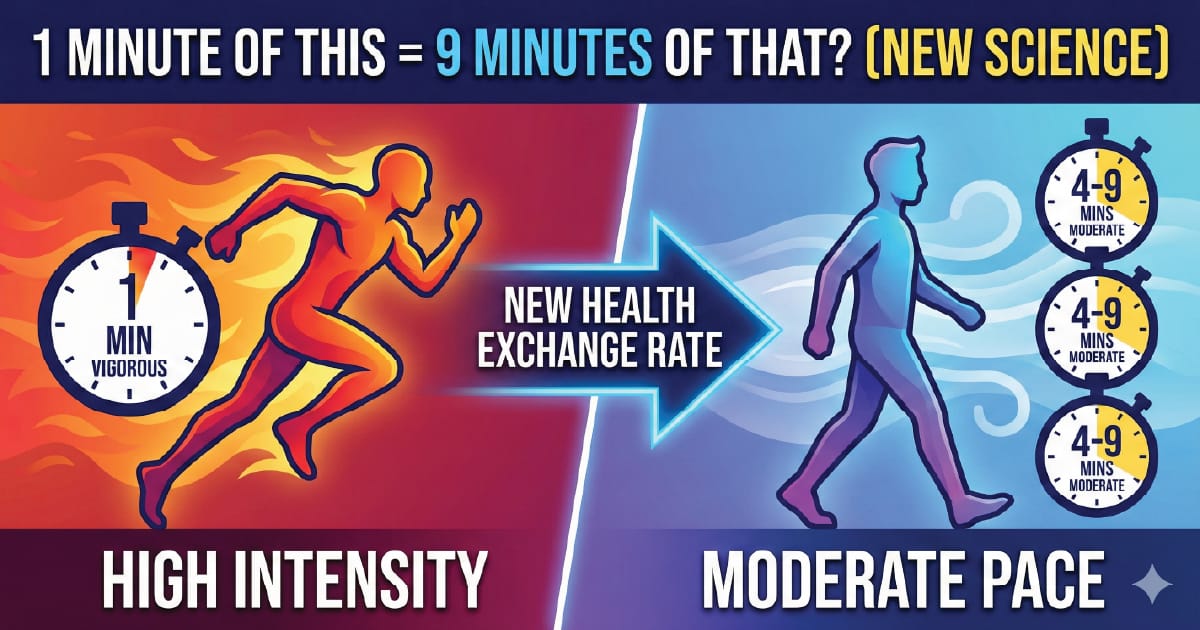
We’ve all heard the old gym math: "1 minute of running equals 2 minutes of walking."
For years, guidelines suggested a simple 2:1 ratio between vigorous and moderate exercise. If you didn't want to jog for 75 minutes, you could walk for 150. Same result, right?
A new study just proved that math wrong. And if you're busy, you’re going to love the correction.
The Study
Researchers analyzed data from over 73,000 people using wearable accelerometers (not just unreliable surveys) and published their findings in Nature Communications. They looked at exactly how much moderate movement you'd need to do to get the same health protection as one minute of vigorous activity.
The Findings
Vigorous physical activity (VPA) is far more potent than we realized. The old 2:1 "exchange rate" is actually much higher depending on the health benefit you want:
For Living Longer: 1 minute of vigorous activity ≈ 4 minutes of moderate activity.
For Heart Health: 1 minute of vigorous activity ≈ 8 minutes of moderate activity.
For Preventing Diabetes: 1 minute of vigorous activity ≈ 9 minutes of moderate activity.
The Health Hack
Stop counting minutes and start counting intensity.
If you are short on time, you can "hack" your way to better health metrics by trading duration for intensity. You don't need a full hour of walking to fight Type 2 diabetes risks; roughly 7 minutes of high-intensity effort (based on the ~1:9 ratio) might give you a similar protective benefit.
Try this:
The Commute Sprint: Walk normally, but power walk or jog up every set of stairs or hill you see.
The Commercial Break: Do burpees or jump rope during ad breaks instead of scrolling on your phone.
Bottom line: Walking is great, but if you can handle the intensity, sweating for just a few minutes pays off like an hour of taking it easy.
THE PROTOCOL
The "Reduced Exertion High-Intensity Interval Training" Method
The Promise: We are all "too busy" to exercise. But what if the biological signal for endurance didn’t require an hour on the treadmill? What if you could get the same mitochondrial adaptation in the time it takes to brew your coffee?
REHIT: This isn't your standard Tabata. This is Reduced Exertion High-Intensity Interval Training. The protocol, popularized by researchers like Dr. Martin Gibala, essentially boils down to:
2 minutes warm-up
20 seconds ALL OUT sprint (100% effort)
2 minutes recovery
20 seconds ALL OUT sprint
2 minutes recovery
20 seconds ALL OUT sprint
3 minutes cool-down
Total time: 10 minutes. Total "work" time: 1 minute.
The Evidence: A landmark study published in PLOS ONE pitted this "One Minute" protocol against a standard 45-minute steady-state cycling session. After 12 weeks, the results were identical.
VO2 Max: Improved by ~19% in both groups.
Insulin Sensitivity: Drastically improved in both groups.
Muscle Cellular Change: Both groups showed significant increases in mitochondrial content.
The Takeaway: It turns out that intensity can substitute for duration. Your body doesn't count the minutes; it measures the stress. 60 seconds of sheer metabolic panic triggers the same survival adaptations as 45 minutes of low-level grinding.
-PEPTIDE OF THE WEEK-
MOTS-c
The "Exercise in a Bottle"?

So far, we’ve focused on the mechanical signal – intense muscular work that pushes your mitochondria to adapt. Now let’s look at the chemical way of sending a similar message: a mitochondrial-derived peptide that can mimic some of the exercise signal from the inside out.
This molecule sounds too good to be true, but it has the science to back it up.
What if you could trigger those same metabolic signals ... without moving a muscle?
Enter MOTS-c, the "exercise mimetic" that is turning the longevity world upside down.
What is MOTS-c?
Most peptides come from our nuclear DNA. MOTS-c is different. It is encoded in the DNA of your mitochondria (the powerhouse of the cell).
Discovered relatively recently at USC, MOTS-c acts as a signaling molecule. When you exercise, your body naturally releases it. It travels to your muscles and tells them: "Hey, we are working out. Burn glucose, increase insulin sensitivity, and build endurance."
The hack? Administering MOTS-c exogenously appears to flip these switches even when you are sedentary.
The Science: Why It’s Called "Exercise in a Bottle"
We don't do hype without data. Here are two landmark studies that put MOTS-c on the map:
1. The "Obesity Stopper" Study (Cell Metabolism, 2015) Researchers found that mice injected with MOTS-c were protected against diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance, even while eating a high-fat diet.
The Hack: The peptide targeted skeletal muscle and enhanced glucose metabolism, effectively mimicking the metabolic effects of exercise.
2. The "Old Mouse, New Tricks" Study (Nature Communications, 2021) This study looked at physical performance. Older mice treated with MOTS-c showed significantly improved physical capacity and grip strength compared to the control group.
The Hack: The study found that MOTS-c levels decline with age in humans, but centenarians (people living to 100+) maintain unusually high levels of it.
Editor’s Note: MOTS-c isn't a replacement for the gym – you still need to move your lymph and build structure. But for metabolic flexibility and endurance, it is a powerhouse tool.
The Bottom Line
If HIIT is the "software hack" for efficient exercise, MOTS-c is the "hardware upgrade" for your mitochondria. It links metabolic stress to metabolic fitness, helping your body process fuel more like a young athlete and less like a sedentary office worker
⚠️ Important Medical & Safety Disclaimer
The content provided in this newsletter is for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
The specific protocols (including REHIT) and compounds (including MOTS-c) discussed herein have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The information presented is not intended to prevent, diagnose, treat, or cure any disease.
Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition, before starting any new diet or exercise program, or before taking any supplements or peptides.
Exercise Risk: High-intensity interval training places significant stress on the cardiovascular system.
Peptide Risk: The long-term effects of many peptides are still under research; use caution and consult a professional.
Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this newsletter. Reliance on any information provided by The Health Hack is solely at your own risk.
-IN THE PRESS-
What we're reading
Is there a tradeoff between muscle size and aerobic capacity?
Can you really be strong and have great cardio? This piece reveals the surprising "ceiling" on muscle size and endurance and why it rarely matters.
https://peterattiamd.com/muscle-strength-and-aerobic-capacity/
New fat-burning diabetes pill protects muscle and appetite
New diabetes pill ignites fat burning in muscle, improves blood sugar and body composition, while preserving appetite and lean mass.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/12/251207031345.htm
Nanomaterial-induced mitochondrial biogenesis enhances intercellular mitochondrial transfer efficiency
Turn stem cells into "mitochondrial biofactories”: nanoflowers that supercharge energy production, repair damaged cells, and hint at future longevity therapies.
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2505237122
Scientists Think We Could "Recharge" Our Cells – And Rewind the Aging Clock
Scientists are using nanomaterials to supercharge cellular "batteries", boosting mitochondrial transfer to rejuvenate damaged cells and potentially slow aging.
https://www.popularmechanics.com/science/health/a69587645/recharging-cells/
More Muscle, Less Belly Fat Slows Brain Aging
Build more muscle, lose hidden belly fat: MRI study links this body combo to younger-looking brains and lower Alzheimer’s risk.
https://www.rsna.org/media/press/2025/2614
New Breakthrough to Strengthen Bone Could Reverse Osteoporosis
Scientists reveal a molecular "on switch” that turbocharges bone-building cells, hinting at future drugs to prevent and even reverse osteoporosis.
https://www.sciencealert.com/new-breakthrough-to-strengthen-bone-could-reverse-osteoporosis
-SCIENTIFIC STUDIES-
New Findings

Are you a "hard gainer" or was it just a bad program?
A fascinating new study in the European Journal of Sport Science suggests your gains (or lack thereof) might be more predictable than you think. Researchers had adults complete two identical 10-week weightlifting blocks separated by a break.
The verdict? Your body’s response to training is highly consistent. If you built muscle easily the first time, you likely will again. However, the study debunked the myth of the total "non-responder"; almost everyone improved in some metric. The catch? Fast gainers also tended to lose muscle quicker during breaks.
-ENTREPRENEURS & STARTUPS-
The Future of Health is Here – and it’s AI-Driven
Editor’s Note: While our goal is to regularly feature exclusive interviews with the boldest entrepreneurs and emerging startups in the space, this week we’re taking a detour to highlight a definitive industry benchmark.
We’re spotlighting Business Insider’s "18 Most Promising Startups in Healthcare of 2025," a curated list that signals exactly where the smart money is flowing.
While this issue of the HEALTH HACK newsletter is focused on mitochondrial mechanics and exercise mimetics, these companies are building the infrastructure that will bring these kinds of interventions into everyday clinics and apps.

When top investors from firms like Kleiner Perkins, Andreessen Horowitz, and Oak HC/FT place their bets, the industry listens. Business Insider recently asked these venture capital giants to identify the breakout companies of 2025 selecting one from their own portfolios and one from outside.
The verdict? The future is automated.
Nearly every startup on this year’s list is leveraging Artificial Intelligence to tackle healthcare’s most persistent headaches: administrative burnout, workforce shortages, and ballooning costs.
What to Watch:
The AI "Scribes": A major focus is on Ambient AI, technology that listens to doctor-patient conversations and automatically generates notes and codes. Ambience Healthcare, heavily backed by the very VCs curating this list, is a prime example of this trend, moving beyond simple transcription to fully automated clinical documentation.
Operational Overhaul: Investors are moving away from pure consumer apps and toward heavy-lifting B2B platforms that solve the "boring" back-end problems of hospital operations and insurance authorizations.
Precision & Speed: From expediting clinical trials to personalizing patient engagement, the chosen 18 are using data to make healthcare faster and more accurate.
We highly recommend reviewing the full roster of 18 companies to see who is defining the landscape of 2025.
Remember!
💡 Mitochondria don’t understand motivation. They only understand signals.
That’s the core idea. It’s not about being "disciplined" or "hard-core”. It’s about sending clear, repeated signals that tell your cells to adapt.
More mitochondria, better function, improved metabolic flexibility, and ultimately, a longer healthspan.
Design your life so those signals show up every day, even in small doses.
Until next time,
Live longer. Upgrade wisely.
Rolf & the HEALTH HACK team
PS: If someone sent you this, you can subscribe here: https://newsletter.health-hack.com