
Hi {{ first name | there}},
Protein is not the problem. Signal is.
Most people try to solve strength, energy, and belly fat with supply-side thinking.
More protein. More supplements. More "biohacks".
This week is a reminder that biology is demand-driven.
If your muscles are "deaf" to protein, the issue is rarely the powder. It's the missing signal: mechanical tension.
If your brain feels fried under sleep debt, the issue is rarely motivation. It's the energy gap – and creatine may help as a buffer.
If visceral fat is the target, the uncomfortable truth is that the best tools are either boring (training, sleep, alcohol control) or medical (and must be treated that way).
Same theme, three angles: you don't get results from ingredients. You get results from signals.
-LONGEVITY PLAYBOOK-
If this helps, consider forwarding it to one person who drinks protein shakes, but doesn't go to the gym.
Subscribe here: https://newsletter.health-hack.com
The "Phantom Muscle" Paradox
Why Your Muscles Can Be "Deaf" to Protein Shakes
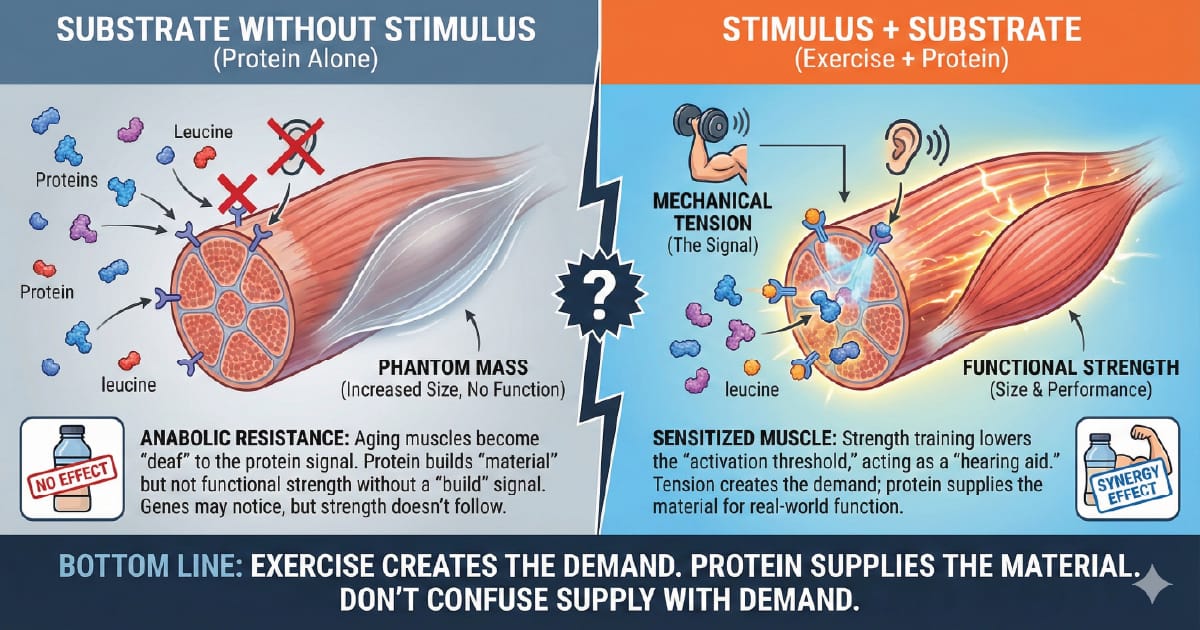
We've been sold a seductive idea: drink the shake → build the muscle.
For many older bodies, it's often biologically insufficient.
Not that protein is useless – substrate without stimulus rarely delivers functional payoff. You can supply all the raw material you want; if the "build" signal is weak, the body doesn't cash the check.
Here’s the newer evidence on why your muscles may be "deaf" to diet – and how to turn the hearing aid on.
The New Evidence: The "Leucine-Only" Test
A new 2026 randomized controlled trial tested the supplement-only hypothesis with serious rigor.
The Setup: Older adults received a large daily dose: ~50.6 g protein enriched with 6 g leucine (the amino acid often called the "anabolic trigger").
The Result (12 weeks): No significant improvements in the outcomes people actually care about:
No meaningful change in muscle size (regional thigh MRI)
No improvement in physical performance (SPPB)
The nuance that matters: This doesn't mean protein is pointless. It means protein + leucine alone didn't translate into measurable size/function gains over 12 weeks in this cohort.
Researchers did see changes in gene-expression markers related to energy production – a hint that biology "noticed" the supplement. But without the right upstream signal, those molecular changes didn't become strength.
The Context: It's Not Just One Study
This result fits a broader pattern in the research:
1. The One-Year Reality Check (CALM Trial, 2021)
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2021) ran a large, year-long trial with five groups: carbohydrate control, collagen protein, whey protein, light resistance training + whey, heavy resistance training + whey.
The Result: Whey alone didn't outperform control on muscle size/strength/function. But heavy resistance training + whey improved quadriceps size and knee extensor strength compared to whey alone.
Translation: Training turns protein into a tool.
2. The “Phantom Muscle” Signal (Meta-analysis, 2023)
Nutrients (2023) pooled randomized trials testing whey protein, leucine, and vitamin D in sarcopenia.
The Study: Effects of Whey Protein, Leucine, and Vitamin D Supplementation in Patients with Sarcopenia
The Finding: Supplements can increase lean mass (appendicular muscle mass).
The Disconnect: Without exercise, those gains often don't translate into better handgrip strength or physical performance (SPPB). With exercise, function improves.
Translation: You can add "material" to muscle, but function is built with a signal.
The Mechanism: Anabolic Resistance
Aging tissues develop anabolic resistance – meaning the muscle-building switch gets less responsive.
Think of muscle protein synthesis like a motion sensor light:
At 20: a small stimulus flips it on.
At 60: you can wave in front of it … and nothing happens.
Leucine helps. Protein helps. But in many older adults, they’re not enough on their own.
What reliably re-sensitizes the system? Mechanical tension.
Strength training lowers the "activation threshold", so protein can actually do its job.
What To Do This Week
Stop trying to buy a solution to a movement problem.
1. The Stimulus (The Driver)
Create mechanical tension 2–3× per week.
The Protocol: Full-body resistance training (machines are fine).
The goal isn't "movement" – it's tension close to fatigue. Aim for sets where the last 1–2 reps feel hard with good form.
2. The Substrate (The Fuel)
Once you're training, protein becomes a multiplier.
The Dose: Aim for ~1.2–1.6 g/kg/day (unless medically contraindicated).
The Tactic: Older muscle responds better to bigger per-meal "boluses".
A practical target is ~0.4 g/kg per meal (often ~30–40 g in one sitting) rather than grazing on small protein snacks all day.
Bottom Line
Exercise creates the demand. Protein supplies the material.
Don’t confuse supply with demand.
THE SUPPLEMENT
Creatine Monohydrate
The Rebrand: It's Not Just for Biceps Anymore
For decades, creatine was pigeonholed as the "meathead powder" – a gym locker staple for squeezing out one extra rep on the bench press.
But a newer wave of research has pushed a rebrand. Creatine is no longer just a muscle supplement. It's increasingly being studied as a bioenergetic buffer for the brain.
If you care about cognitive longevity, mental clarity under fatigue, and physical resilience, creatine monohydrate is one of the safest, cheapest, and most evidence-backed supplements you can buy.
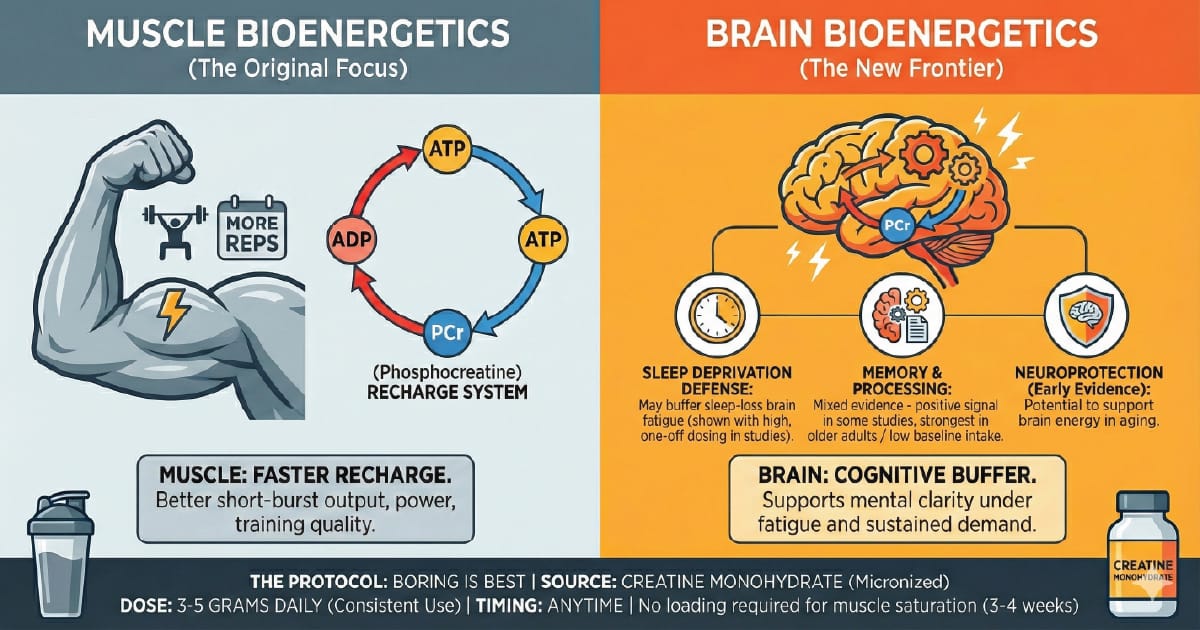
The Mechanism: Energy for Expensive Tissue
Your body runs on ATP (adenosine triphosphate). When you spend energy, ATP breaks down into ADP (adenosine diphosphate). To keep performing, you need to recycle ADP back into ATP fast.
Creatine helps via the phosphocreatine system – a rapid "recharge" pathway for ATP.
In muscles: better short-burst output – more reps, more power, better training quality.
In the brain: when energy demand spikes (sleep loss, sustained mental work), creatine appears to help as a buffer during that metabolic crunch.
The New Science: "From the Neck Up"
Recent trials and reviews have shifted some attention from the gym to the office:
1. Sleep deprivation defense
A 2024 trial found that a single high dose of creatine could partially offset cognitive decline during sleep deprivation, alongside measurable shifts in brain energy metabolites. Translation: it can act like a backup battery when sleep debt hits.
Note (dose nuance): Most people don't need high doses for day-to-day use. But the sleep-deprivation studies used a much larger, one-off dose (about 0.35 g/kg, often ~20-30 g). Translation: the "all-nighter buffer" effect seems to require acute high dosing, not your everyday maintenance dose.
2. Memory and processing
A 2025 systematic review in older adults found a generally positive signal (especially memory and attention), but the evidence base is mixed – it includes both supplementation trials and observational studies. Translation: promising, not settled.
3. Neuroprotection (early)
There is plausible but still early evidence that creatine could support brain energy metabolism in aging. Treat this as a "watch this space" signal, not a proven anti-dementia intervention.
The Protocol: Boring Is Best
Ignore the hype: "Creatine HCL", "buffered creatine", and liquid serums are usually marketing solutions looking for a biological problem.
The source: Creatine monohydrate (micronized if you want easier mixing).
The dose: 3-5 grams daily.
The timing: doesn't matter. Consistency matters.
The loading phase (optional):
Classic loading: ~20 g/day for 5-7 days (split doses), then 3-5 g/day
Pros: saturates muscle stores faster
Cons: GI upset in some people
No-loading option: 3-5 g/day typically reaches saturation in roughly 3-4 weeks
Caveats and Myths
Water retention: you may gain a little water weight early on. This is mostly intracellular (inside the muscle cell), not "puffy under the skin" bloating.
Kidney damage: in healthy people at normal doses, the overall evidence does not show harm to kidney function. One nuance: serum creatinine can rise slightly, which can look scary on labs, but does not automatically mean kidney damage. If you have kidney disease or abnormal renal labs, talk to your clinician first.
Hair loss: the fear largely traces back to an older small study suggesting higher DHT. A newer randomized controlled trial directly measuring hair parameters found no meaningful differences versus placebo. Translation: for most people, this is very unlikely to be an issue.
Scientific Studies
1. Creatine and sleep deprivation (The Brain Battery)
Single dose creatine improves cognitive performance and induces changes in cerebral high energy phosphates during sleep deprivation
Verdict: A single high dose partially offset cognitive decline during sleep deprivation and was associated with measurable shifts in brain energy metabolites.
2. Creatine and cognitive aging
Creatine and Cognition in Aging: A Systematic Review of Evidence in Older Adults
Verdict: Across 6 studies (n = 1542), the overall signal is positive for cognition (especially memory and attention), but the evidence base is mixed and higher-quality trials are still needed.
3. Creatine and hair loss
Does creatine cause hair loss? A 12-week randomized controlled trial
Verdict: No significant differences in DHT or hair growth parameters versus placebo.
-IN THE PRESS-
What we're reading
Studies link some food preservatives to higher diabetes and cancer risk
Black gold: The vitamin-packed fruit that regulates blood sugar and blood pressure
What’s the right way to define ultra-processed foods?
AI Brain Model Shows How Neurons Learn, and Where They Fail
Scientists Think They’ve Discovered How Humans Could Recover Lost Vision
-PEPTIDE OF THE WEEK-
Tesamorelin
The "Sniper" for Visceral Fat
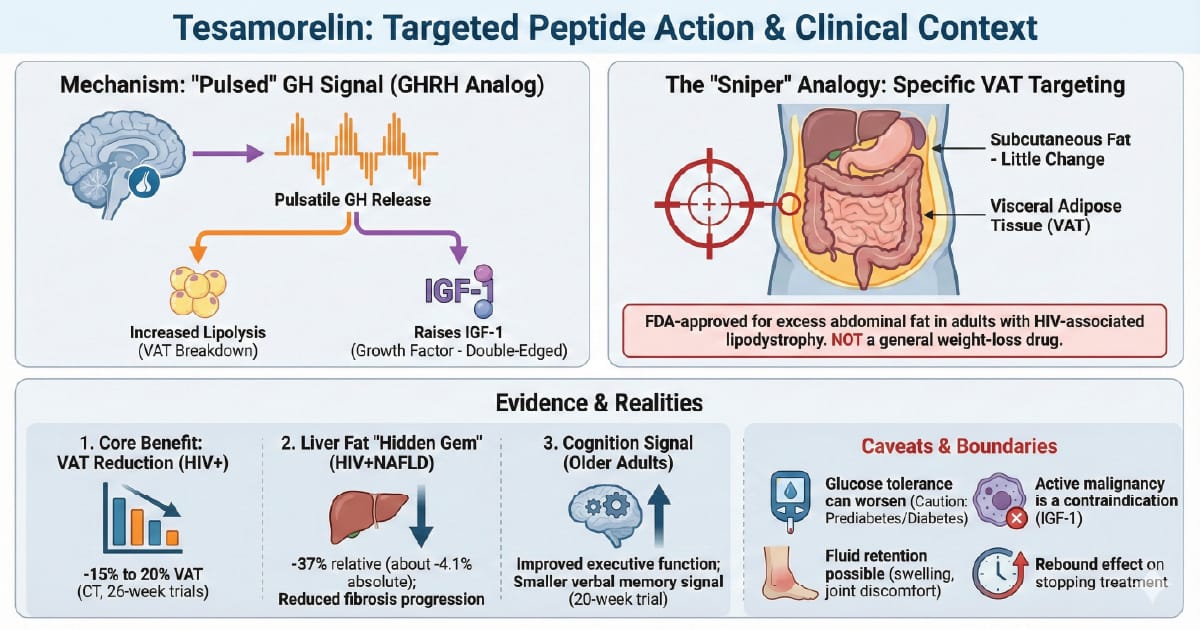
If Ozempic is the carpet bomb for weight loss, Tesamorelin is the sniper rifle.
But the sniper shot is aimed at one target: visceral fat – and the strongest evidence is in HIV-associated lipodystrophy (it is FDA-approved there, not as a general weight-loss drug).
Important boundary: tesamorelin is FDA-approved to reduce excess abdominal fat in adults with HIV-associated lipodystrophy. It is not indicated for weight loss, and the long-term cardiovascular outcome story is still not settled. Off-label use exists, but the strongest data live in that HIV population.
The Mechanism: A "Pulsed" Growth Hormone Signal
Tesamorelin is a GHRH analog (growth hormone-releasing hormone).
HGH injection – adds exogenous growth hormone directly and can produce more "always-on" exposure.
Tesamorelin – stimulates your pituitary to release your own GH in a more physiologic, pulsatile pattern.
Downstream, this tends to:
Increase lipolysis (fat breakdown), with a notable effect in visceral adipose tissue (VAT) in trials
Raise IGF-1 (a growth factor), which is a double-edged sword: it may support repair, but it also requires caution and monitoring
What The Evidence Actually Shows
1) The Core Benefit – Visceral Fat Reduction
In the landmark 26-week trials that led to approval, tesamorelin reduced visceral adipose tissue on CT by about 15% to 20% versus placebo.
Key nuance: subcutaneous fat (the pinchable stuff) changed little. This is not a general "scale weight" drug. It's a VAT remodeling drug in the population studied.
2) Liver Fat – The Legit "Hidden Gem" (In HIV + NAFLD)
A randomized multicenter trial in people with HIV and NAFLD found tesamorelin:
reduced liver fat (about -4.1% absolute, roughly -37% relative from baseline)
reduced the progression of fibrosis during the treatment period
Translation: in this specific clinical setting, tesamorelin looked like a credible liver-fat reduction tool, not a "detox".
3) Cognition – Interesting Signal, Not A Promise
A 20-week trial using a GHRH analog (tesamorelin) in older adults found improvements in executive function, with a smaller signal for verbal memory.
Translation: intriguing "brain metabolism" territory, but far from a guaranteed cognitive longevity intervention.
Reality Check: Who This Is (And Is Not) For
Tesamorelin is not a "longevity supplement". It's a prescription peptide with real data in a defined medical population, real cost, and real monitoring requirements.
If someone is considering it off-label, the "health hack" is not a DIY protocol. The hack is asking the right questions and tracking the right risks.
Caveats That Matter
Glucose: GH signaling can worsen glucose tolerance in some people. If you are prediabetic or diabetic, this is a serious discussion.
IGF-1 and cancer risk: Active malignancy is a contraindication. Prior cancer requires careful clinician judgment.
Fluid retention: Can occur (swelling, joint discomfort).
Rebound: When treatment stops, VAT benefits can fade unless lifestyle supports the new baseline.
What To Do This Week (Even If You Never Touch A Peptide)
If VAT is your target, run the boring, high-signal basics for 14 days:
Measure one thing: waist circumference at the navel, 2x/week (same time, same conditions).
Lift 2-3x/week: full-body strength, close to fatigue (VAT responds to improved muscle insulin sensitivity).
Cut the silent VAT accelerators: alcohol + sleep debt for one week. Both reliably worsen abdominal fat biology.
Scientific References
Visceral fat reduction (26-week RCT, NEJM)
Metabolic effects of a growth hormone-releasing factor in patients with HIVLong-term safety and durability (52 weeks, then loss after stopping)
Long-term safety and effects of tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing factor analogue, in HIV patients with abdominal fat accumulationLiver fat and fibrosis progression (HIV + NAFLD, Lancet HIV 2019)
Effects of tesamorelin on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in HIV: a randomised, double-blind, multicentre trialCognition trial (GHRH analog in older adults, 20 weeks)
Effects of growth hormone–releasing hormone on cognitive function in adults with mild cognitive impairment and healthy older adults: results of a controlled trial
⚠️ Disclaimer: Tesamorelin is a prescription drug (FDA-approved only for reducing excess abdominal fat in adults with HIV-associated lipodystrophy). Any off-label use for "longevity" or visceral fat is experimental and should be treated as a monitored medical decision. It can raise IGF-1 and may worsen glucose tolerance. Avoid if pregnant/breastfeeding, with active (or suspected) malignancy, uncontrolled diabetes, or serious endocrine disease. Do not self-source peptides. Purity, dosing, and storage are the primary risks. Educational content only – not medical advice.
Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this newsletter.
QUICK POLL
Last week, most of you said the biggest challenge is simply not knowing which lever matters most. This week, let's get more specific: what's the main strength lever that breaks for you?
What's your biggest bottleneck right now for getting stronger?
LAST WEEK'S POLL RESULTS
Which lever do you think matters most for getting January back on track?
28.6% 🌞 Light timing (when I see daylight)
12.1% ⏰ Meal timing (when I eat)
8.8% 🌡️ Temperature cues (heat → cooling)
18.7% 🧠 Stress / nervous-system regulation
31.8% 🤷♂️ I don’t know – that’s why I’m here
QUOTE TO REMEMBER
💡 Your body doesn't respond to supplies. It responds to demand.
If you only do three things after reading this, do these:
Create the signal – 2 strength sessions this week, full-body, last 1-2 reps hard with clean form.
Support the signal – hit your protein in real meals (aim for one meal today with 30-40 g).
Protect your energy – if sleep is short, consider creatine as a low-risk "backup battery" habit (3-5 g/day).
And if belly fat is your obsession, stop guessing – measure your waist twice this week. What gets measured gets managed.
Until next time,
Live longer. Upgrade wisely.
Rolf & the HEALTH HACK team
PS: If someone sent you this, you can subscribe here: https://newsletter.health-hack.com