
The Metabolic U-Turn
Hi {{ first name | there}},
Boxing Day is the annual metabolic hangover.
Not just the sugar – the stagnation too. You likely ran a predictable experiment: caloric surplus + prolonged sitting + circadian disruption.
Today’s goal isn’t penance. We don’t do guilt here.
The goal is disposal: manually operate the machinery that moves fuel out of your blood and into your muscle tissue.
Let’s do a u-turn.
Do this today:
20–60 min after your biggest meal: 90 seconds of squats or a wall sit.
Optional: 10 min before a starchy meal: 1 tbsp ACV in water.
QUICK POLL
Be honest – what feels most broken right now?
⚠️ Next week we’ll share the poll results and the top reader strategies.
LAST WEEK'S POLL RESULTS
What is your primary defense strategy for the Big Feast?
26.2% The Full Shield: I’m stacking all three (Walk + Spice + Order).
16.4% The 10-Minute Walk: I'll excuse myself immediately after dessert.
24.6% The Cinnamon Buffer: I'm trusting the chemistry (capsules ready).
24.4% The "Food Order" Stack: Veggies first, protein second, pie last.
8.2% Pure Chaos: I am accepting the glucose spike and the nap.
-LONGEVITY PLAYBOOK-
If this helps, forward it to one person currently living off leftovers.
Subscribe here: https://newsletter.health-hack.com
The "Sugar Sponge" Technique
Hacking GLUT4 translocation to clear glucose (even when insulin signaling is sluggish)
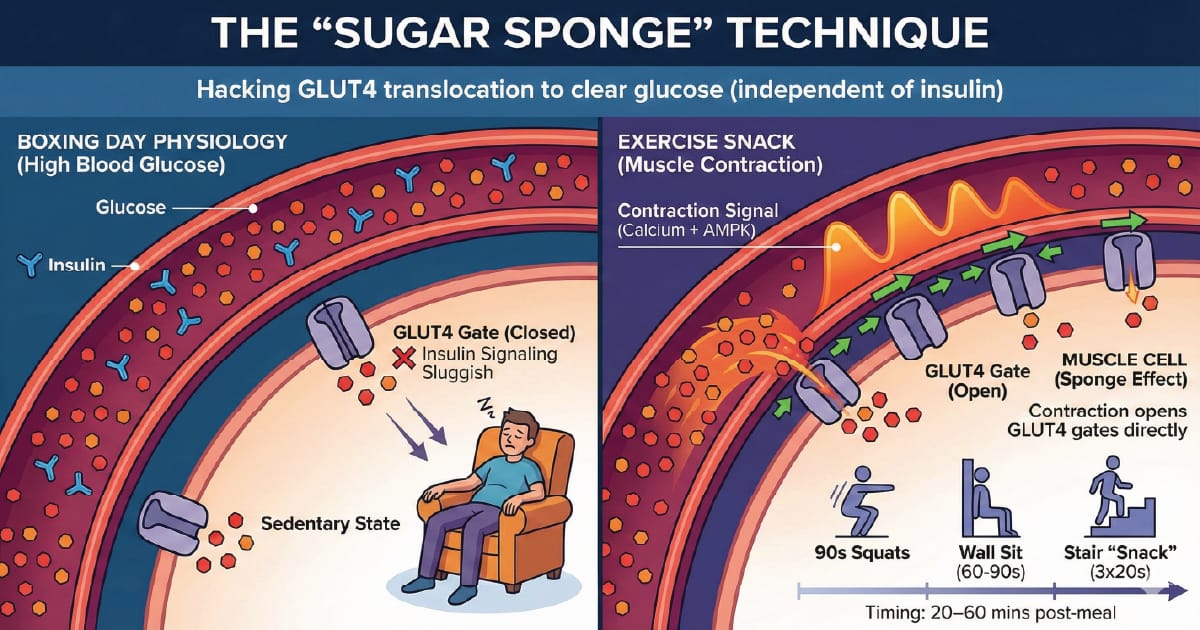
The Problem (Boxing Day physiology)
After days of feasting + sitting, your muscles can be closer to "storage saturation" (glycogen is topped up), and your body is more likely to handle the next carb hit with a larger glucose + insulin excursion than it would on a normal week. Breaking up prolonged sitting with short activity breaks has repeatedly been shown to improve post-meal glucose (and often insulin) compared with uninterrupted sitting.
The lever most people ignore
Your muscle cells have glucose gates called GLUT4. Insulin can open them – but so can muscle contraction, via signaling pathways that are at least partly insulin-independent (think calcium signaling + AMPK). Translation: you can increase glucose uptake without needing a perfect "willpower day".
The evidence (what’s solid)
A 2025 systematic review/meta-analysis in adults with obesity quantified the acute effects of brief, frequent interruptions to sitting ("exercise snacks") and found meaningful improvements in postprandial glucose and insulin outcomes vs uninterrupted sitting.
A 2024 controlled trial in overweight/obese men found that short, frequent walking or squatting breaks improved glycemic control more than one single bout of walking within prolonged sitting.
The execution: The "90-Second Soak"
You don’t need a 30-minute cardio session. You need high-tension contraction – a loud metabolic signal.
Choose one:
Air squats: continuous for 90 seconds (slow = harder)
Wall sit: hold 60–90 seconds (shake = signal delivered)
Stair "snack": 3 x 20 seconds hard (if you have stairs)
If squats hurt your knees/back, do a brisk incline walk, step-ups, or fast chair-stands instead.
Timing: aim for 20–60 minutes after your biggest meal. Don’t obsess over the exact minute – the win is "soon after", not "sometime later".
Why it works (one sentence): contraction creates an immediate local energy demand – the muscle pulls glucose in by moving GLUT4 to the surface – you "sponge" glucose into muscle instead of letting it linger.
THE PROTOCOL
The "Biochemical Brake" (for when you’re definitely eating leftovers today)
This is not a detox. It’s a simple curve-flattener.
The ACV + food-order pre-load
10 minutes before a high-starch meal:
Mix 1 tbsp (15 ml) apple cider vinegar into a tall glass of water.
Drink it (optional: through a straw).
Eat fiber/protein first, carbs last.
What the evidence says: meta-analyses of clinical trials suggest vinegar can reduce postprandial glucose and insulin responses, indicating it can be a useful adjunct for glycemic control (effects vary by person and meal).
Mechanism (most defensible): multiple studies suggest vinegar’s effects on starchy meals may be partly explained by slower gastric emptying.
Practical nuance: this tends to be most useful for starchy meals (potatoes, bread, pasta). It won’t "cancel" candy.
Warnings (keep it smart):
Teeth: rinse with water after; don’t sip acidic drinks all day.
Reflux: if vinegar reliably worsens symptoms, skip it.
On GLP-1 meds / delayed gastric emptying: don’t pile "slowing tools" on top of each other without clinician advice.
-PEPTIDE OF THE WEEK-
Oral Wegovy (semaglutide 25 mg)
The first weight-loss GLP-1 pill – FDA-approved (Dec 22, 2025)

This week’s "peptide" just graduated from the lab to the pharmacy: the FDA approved once-daily oral semaglutide 25 mg for chronic weight management. Novo Nordisk announced the approval on December 22, 2025, and multiple outlets reported an early January 2026 U.S. launch expectation.
The data (OASIS 4)
In the primary trial analysis, the estimated mean change in body weight from baseline to week 64 was -13.6% with oral semaglutide vs -2.2% with placebo.
Trade coverage and the company’s release also report an "if all patients stayed on treatment" figure around 16.6% (different estimand = different number; both can be true).
The reality check (anti-hype)
The convenience tax: the pill is high-maintenance. The FDA label specifies: take in the morning on an empty stomach with water only (no more than 4 ounces) and wait at least 30 minutes before eating/drinking/other oral meds.
Side effects: GI issues are the common class effect. The Wegovy tablets label reports severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions in 2% of tablet-treated vs 0% of placebo patients.
⚠️ Disclaimer: This newsletter is educational, not medical advice. GLP-1 therapy is a clinician decision.
Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this newsletter.
-IN THE PRESS-
What we're reading
The Future of Fitness: ACSM Announces Top Trends for 2026
Track the 2026 fitness wave: wearables, active aging, weight management and mental health trends reshaping how we move and thrive.
https://acsm.org/top-fitness-trends-2026/
Just 2 short bursts of exercise a day could boost heart and lung fitness
Turn stairs, brisk walks, or quick squats into "exercise snacks" that measurably improve fitness – without changing your daily routine.
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/exercise-snacks-boost-heart-and-lung-health
First-Ever Human Trial Finds Fasting Mimicking Diet Enhances Autophagy While Improving Metabolic Health
Five-day fasting-mimicking diet boosts cellular "clean-up", improves weight, blood sugar and insulin sensitivity in first-ever human autophagy trial.
https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/first-ever-human-trial-finds-fasting-mimicking-diet-enhances-autophagy-while-improving-metabolic-health-302643077.html
New study shows some plant-based diets may raise heart disease risk
Ultra-processed "plant-based" foods may quietly raise heart disease risk by 40%. Discover which plant foods actually protect your heart.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/12/251214100928.htm
Adding Black Cumin to Your Diet May Lower Bad Cholesterol and Calm Inflammation
Tiny seed, big impact: discover how daily black cumin may lower cholesterol, tame inflammation, and support weight and metabolic health.
https://www.verywellhealth.com/black-cumin-seeds-and-anti-obesity-effect-study-11865058
How C-reactive protein outpaced "bad" cholesterol as leading heart disease risk marker
C-reactive protein now tops bad cholesterol as the key heart disease predictor – measure inflammation via simple blood test for better risk insight.
https://theconversation.com/how-c-reactive-protein-outpaced-bad-cholesterol-as-leading-heart-disease-risk-marker-271143
-SCIENTIFIC STUDIES-
New Findings

Exercise Hits the "Hallmarks of Aging" (Not Just "Cardio")
A Dec 2025 open-access review argues that regular physical activity is linked to healthy aging and can mitigate multiple core "hallmarks of biological aging" – including mitochondrial dysfunction, impaired macroautophagy, deregulated nutrient sensing, cellular senescence, chronic inflammation, and more. It also emphasizes that reducing sedentary time plus consistent activity should be encouraged across all ages, while researchers still work on defining minimum effective and maximum safe thresholds in older adults.
Takeaway: Your 90-second "signal" is not a gimmick – it fits the broader biology of "exercise as anti-aging medicine," especially when it breaks up sitting.
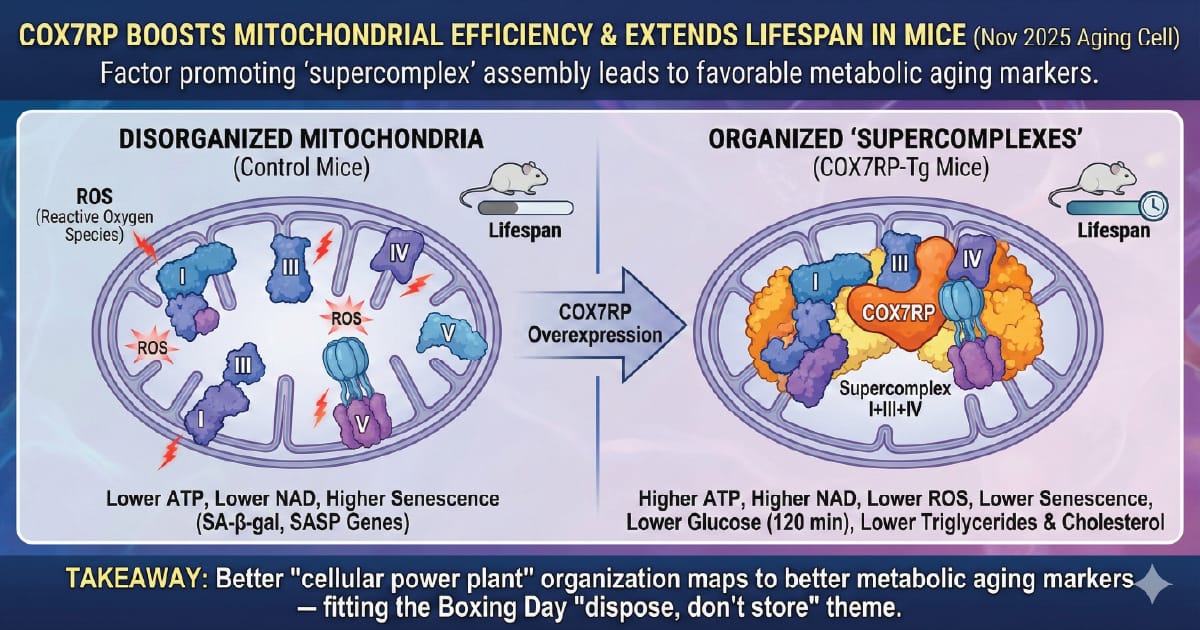
COX7RP Boosts Mitochondrial Efficiency – and Extends Lifespan in Mice
A Nov 2025 Aging Cell paper reports that COX7RP (a factor that helps assemble mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes into "supercomplexes") was linked to a significant lifespan extension in COX7RP-transgenic mice. The authors also report a more favorable metabolic profile – including lower blood glucose at 120 minutes on a glucose tolerance test (without a significant AUC difference), lower triglycerides and total cholesterol, higher ATP and NAD levels, lower ROS, and lower senescence-associated beta-gal levels. They also found downregulation of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) genes in older white adipose tissue, particularly in adipocytes.
Takeaway: Better "cellular power plant" organization maps to better metabolic aging markers, which is exactly the theme of this Boxing Day "dispose, don't store" edition.
Remember!
💡 You don’t need a detox tea. You need a signal.
Your body is waiting for instructions.
Sitting tells it to store. Movement tells it to dispose.
Move the sugar, don’t store it.
Until next time,
Live longer. Upgrade wisely.
Rolf & the HEALTH HACK team
PS: If someone sent you this, you can subscribe here: https://newsletter.health-hack.com